System Alpha - ISM Controls Implementation
Visual representation of ISM controls and their implementation status
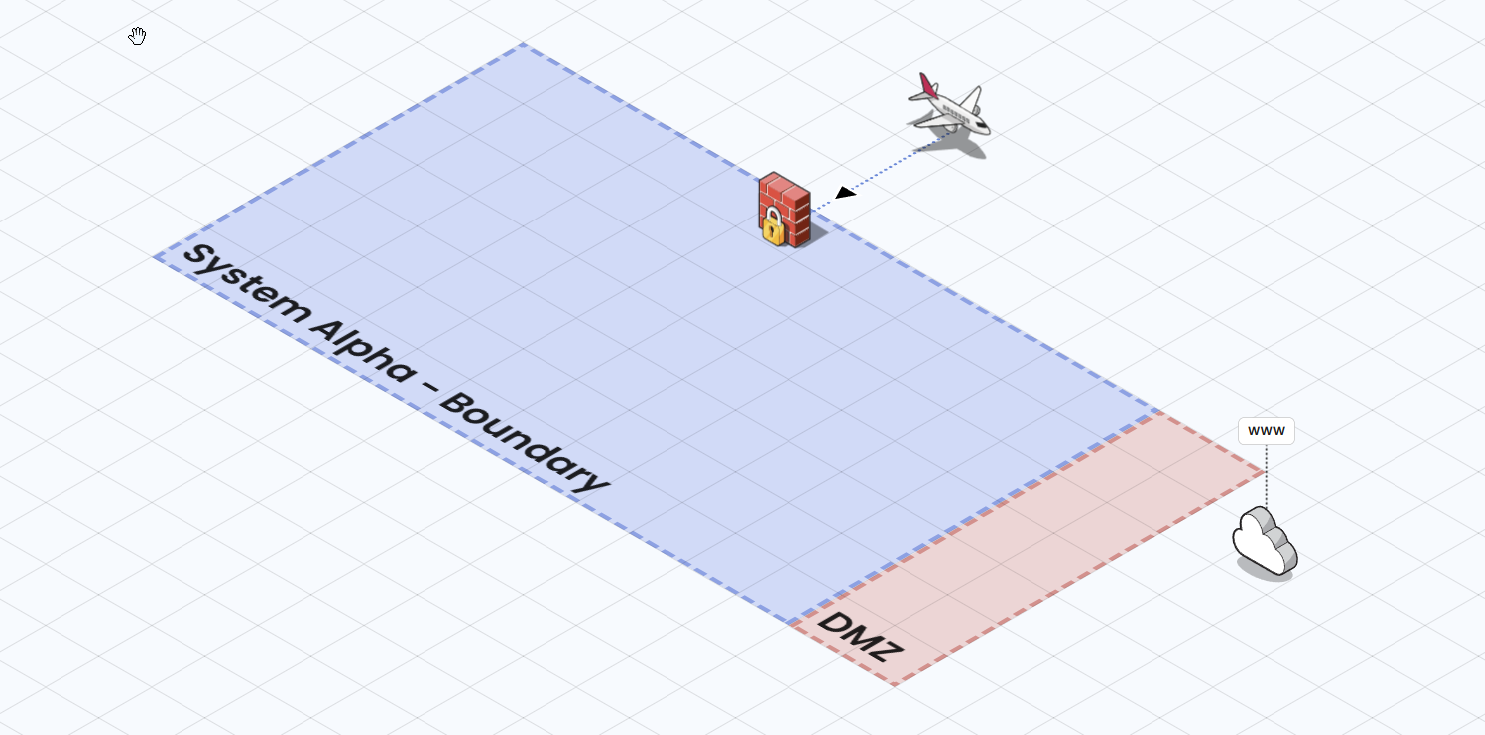
System Architecture Overview (actual pic coming soon)
Document Pack
System Security Plan
Comprehensive security documentation for the system
SSP Annex-A
Detailed security control implementation annex
In Progress
Cyber Incident Response Plan
Procedures for responding to security incidents
Change and Configuration Management Plan
Processes for managing system changes and configurations
Continuous Monitoring Plan
Ongoing security monitoring and assessment procedures
Security Assessment Report
Results of security control assessments
Plan of Action and Milestones
Remediation plan for identified security weaknesses
Guidelines for cybersecurity roles
40 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
40 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1997 | The board of directors or executive committee defines clear roles and responsibilities for cybersecurity both within the board of directors or executive committee and broadly within their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1998 | The board of directors or executive committee ensures that cybersecurity is integrated throughout all business functions within their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1999 | The board of directors or executive committee ensures the cybersecurity strategy for their organisation is aligned with the overarching strategic direction and business strategy for their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2000 | The board of directors or executive committee seeks regular briefings or reporting on the cybersecurity posture of their organisation, as well as the threat environment in which they operate, from internal and external subject matter experts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2001 | The board of directors or executive committee champions a positive cybersecurity culture within their organisation, including through leading by example. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2002 | The board of directors or executive committee maintains a sufficient level of cybersecurity literacy to fulfil both their fiduciary duties and any legislative or regulatory obligations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2003 | The board of directors or executive committee maintains awareness of key cybersecurity recruitment activities, retention rates for cybersecurity personnel, and cybersecurity skills and experience gaps within their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2004 | The board of directors or executive committee supports the development of cybersecurity skills and experience for all personnel via internal and external cybersecurity awareness raising and training opportunities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2005 | The board of directors or executive committee understands the business criticality of their organisation’s systems, including at least a basic understanding of what exists, their value, where they reside, who has access, who might seek access, how they are protected, and how that protection is verified. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2006 | The board of directors or executive committee plans for major cybersecurity incidents, including by participating in exercises, and understand their duties in relation to such cybersecurity incidents. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0714 | A CISO is appointed to provide cybersecurity leadership and guidance for their organisation (covering information technology and operational technology). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1478 | The CISO oversees their organisation’s cybersecurity program and ensures their organisation’s compliance with cybersecurity policy, standards, regulations and legislation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1617 | The CISO regularly reviews and updates their organisation’s cybersecurity program to ensure its relevance in addressing cyberthreats and harnessing business and cybersecurity opportunities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1966 | The CISO develops, implements, maintains and verifies on a regular basis a register of systems used by their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0724 | The CISO implements cybersecurity measurement metrics and key performance indicators for their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0725 | The CISO coordinates cybersecurity and business alignment through a cybersecurity steering committee or advisory board, comprising of key cybersecurity and business executives, which meets formally and on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0726 | The CISO coordinates security risk management activities between cybersecurity and business teams. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0718 | The CISO regularly reports directly to their organisation’s board of directors or executive committee on cybersecurity matters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1918 | The CISO regularly reports directly to their organisation’s audit, risk and compliance committee (or equivalent) on cybersecurity matters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0733 | The CISO is fully aware of all cybersecurity incidents within their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1618 | The CISO oversees their organisation’s response to cybersecurity incidents. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0734 | The CISO contributes to the development, implementation and maintenance of business continuity and disaster recovery plans for their organisation to ensure that business-critical services are supported appropriately in the event of a disaster. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0720 | The CISO oversees the development, implementation and maintenance of a cybersecurity communications strategy to assist in communicating the cybersecurity vision and strategy for their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0731 | The CISO oversees cyber supply chain risk management activities for their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0732 | The CISO receives and manages a dedicated cybersecurity budget for their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0717 | The CISO oversees the management of cybersecurity personnel within their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2020 | The CISO ensures sufficient cybersecurity personnel, with the right skills and experience, are acquired to support cybersecurity activities within their organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0735 | The CISO oversees the development, implementation and maintenance of their organisation’s cybersecurity awareness training program. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1071 | Each system has a designated system owner. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1525 | System owners register each system with its authorising officer. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1633 | System owners, in consultation with each system’s authorising officer, determine the system boundary, business criticality and security objectives for each system based on an assessment of the impact if it were to be compromised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1203 | System owners, in consultation with each system’s authorising officer, conduct a threat and risk assessment for each system. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1634 | System owners, in consultation with each system’s authorising officer, select controls for each system and tailor them to achieve desired security objectives. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0009 | System owners, in consultation with each system’s authorising officer, identify any supplementary controls required based upon the unique nature of each system, its operating environment and the organisation’s risk tolerances. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1635 | System owners implement controls for each system and its operating environment. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1636 | System owners, in consultation with each system’s authorising officer, ensure controls for each non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive, PROTECTED and SECRET system and its operating environment undergo a security assessment by their organisation’s own assessors or Infosec Registered Assessor Program (IRAP) assessors to determine if they have been implemented correctly and are operating as intended. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0027 | System owners obtain authorisation to operate each non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive, PROTECTED and SECRET system from its authorising officer based on the acceptance of the security risks associated with its operation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1526 | System owners monitor each system, and associated cyberthreats, security risks and controls, on an ongoing basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2021 | System owners implement and maintain data minimisation practices for each of their systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1587 | System owners report the security status of each system to its authorising officer at least annually. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for cybersecurity incidents
22 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
22 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0576 | A cybersecurity incident management policy, and associated cybersecurity incident response plan, is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1784 | The cybersecurity incident management policy, including the associated cybersecurity incident response plan, is exercised at least annually. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0125 | A cybersecurity incident register is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1803 | A cybersecurity incident register contains the following for each cybersecurity incident: - the date the cybersecurity incident occurred - the date the cybersecurity incident was discovered - a description of the cybersecurity incident - any actions taken in response to the cybersecurity incident - to whom the cybersecurity incident was reported. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1625 | An insider threat mitigation program is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1626 | Legal advice is sought regarding the development and implementation of an insider threat mitigation program. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0120 | Cybersecurity personnel have access to sufficient data sources and tools to ensure that systems can be monitored for key indicators of compromise. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0123 | Cybersecurity incidents are reported to the chief information security officer, or one of their delegates, as soon as possible after they occur or are discovered. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0140 | Cybersecurity incidents are reported to ASD as soon as possible after they occur or are discovered. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1880 | Cybersecurity incidents that involve customer data are reported to customers and the public in a timely manner after they occur or are discovered. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1881 | Cybersecurity incidents that do not involve customer data are reported to customers and the public in a timely manner after they occur or are discovered. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1819 | Following the identification of a cybersecurity incident, the cybersecurity incident response plan is enacted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0133 | When a data spill occurs, data owners are advised and access to the data is restricted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0917 | When malicious code is detected, the following steps are taken to handle the infection: - the infected systems are isolated - all previously connected media used in the period leading up to the infection are scanned for signs of infection and isolated if necessary - antivirus applications are used to remove the infection from infected systems and media - if the infection cannot be reliably removed, systems are restored from a known good backup or rebuilt. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1969 | Malicious code, when stored or communicated, is treated beforehand to prevent accidental execution. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1970 | Malicious code processed for cybersecurity incident response or research purposes is done so in a dedicated analysis environment that is segregated from other systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0137 | Legal advice is sought before allowing intrusion activity to continue on a system for the purpose of collecting further data or evidence. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1609 | System owners are consulted before allowing intrusion activity to continue on a system for the purpose of collecting further data or evidence. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1731 | Planning and coordination of intrusion remediation activities are conducted on a separate system to that which has been compromised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1732 | To the extent possible, all intrusion remediation activities are conducted in a coordinated manner during the same planned outage. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1213 | Following intrusion remediation activities, full network traffic is captured for at least seven days and analysed to determine whether malicious actors have been successfully removed from the system. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0138 | The integrity of evidence gathered during an investigation is maintained by investigators: - recording all of their actions - maintaining a proper chain of custody - following all instructions provided by relevant law enforcement agencies. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for procurement and outsourcing
35 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
35 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1631 | Suppliers of operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services associated with systems are identified. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1452 | A supply chain risk assessment is performed for suppliers of operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services in order to assess the impact to a system’s security risk profile. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1567 | Suppliers identified as high risk by a cyber supply chain risk assessment are not used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1568 | Operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are procured from suppliers that have demonstrated a commitment to the security of their products and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1882 | Operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are procured from suppliers that have demonstrated a commitment to transparency for their products and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1632 | Operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are procured from suppliers that have a strong track record of maintaining the security of their own systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1569 | A shared responsibility model is created, documented and shared between suppliers and their customers in order to articulate the security responsibilities of each party. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1785 | A supplier relationship management policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1786 | An approved supplier list is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1787 | Operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are sourced from approved suppliers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1788 | Multiple potential suppliers are identified for sourcing critical operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1789 | Sufficient spares of critical IT equipment and OT equipment are sourced and kept in reserve. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1790 | Operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are delivered in a manner that maintains their integrity. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1791 | The integrity of operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are assessed as part of acceptance of products and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1792 | The authenticity of operating systems, applications, IT equipment, OT equipment and services are assessed as part of acceptance of products and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1736 | A managed service register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1737 | A managed service register contains the following for each managed service: - managed service provider’s name - managed service’s name - purpose for using the managed service - sensitivity or classification of data involved - due date for the next security assessment of the managed service - contractual arrangements for the managed service - point of contact for users of the managed service - 24/7 contact details for the managed service provider. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1793 | Managed service providers and their non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive, PROTECTED and SECRET managed services undergo an Infosec Registered Assessor Program (IRAP) assessment, using the latest release of the ISM available prior to the beginning of the IRAP assessment (or a subsequent release), at least every 24 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1637 | An outsourced cloud service register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1638 | An outsourced cloud service register contains the following for each outsourced cloud service: - cloud service provider’s name - cloud service’s name - purpose for using the cloud service - sensitivity or classification of data involved - due date for the next security assessment of the cloud service - contractual arrangements for the cloud service - point of contact for users of the cloud service - 24/7 contact details for the cloud service provider. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1570 | Outsourced cloud service providers and their non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive, PROTECTED and SECRET cloud services undergo an IRAP assessment, using the latest release of the ISM available prior to the beginning of the IRAP assessment (or a subsequent release), at least every 24 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1395 | Service providers, including any subcontractors, provide an appropriate level of protection for any data entrusted to them or their services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0072 | Security requirements associated with the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data are documented in contractual arrangements with service providers and reviewed on a regular and ongoing basis to ensure they remain fit for purpose. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1571 | The right to verify compliance with security requirements is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1738 | The right to verify compliance with security requirements documented in contractual arrangements with service providers is exercised on a regular and ongoing basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1804 | Break clauses associated with failure to meet security requirements are documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0141 | The requirement for service providers to report cybersecurity incidents to a designated point of contact as soon as possible after they occur or are discovered is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1794 | A minimum notification period of one month by service providers for significant changes to their own service provider arrangements is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1451 | Types of data and its ownership is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1572 | The regions or availability zones where data will be processed, stored and communicated, as well as a minimum notification period for any configuration changes, is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1573 | Access to all logs relating to an organisation’s data and services is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1574 | The storage of data in a portable manner that allows for backups, service migration and service decommissioning without any loss of data is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1575 | A minimum notification period of one month for the cessation of any services by a service provider is documented in contractual arrangements with service providers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1073 | An organisation’s systems are not accessed or administered by a service provider unless a contractual arrangement exists between the organisation and the service provider to do so. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1576 | If an organisation’s systems are accessed or administered by a service provider in an unauthorised manner, the organisation is immediately notified. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for cybersecurity documentation
11 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
11 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0039 | A cybersecurity strategy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0047 | Organisational-level cybersecurity documentation is approved by the chief information security officer while system-specific cybersecurity documentation is approved by the system’s authorising officer. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1739 | A system’s security architecture is approved prior to the development of the system. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0888 | Cybersecurity documentation is reviewed at least annually and includes a ‘current as at \[date\]’ or equivalent statement. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1602 | Cybersecurity documentation, including notification of subsequent changes, is communicated to all stakeholders. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0041 | Systems have a system security plan that includes an overview of the system (covering the system’s purpose, the system boundary and how the system is managed) as well as an annex that covers applicable controls from this document and any additional controls that have been identified and implemented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0043 | Systems have a cybersecurity incident response plan that covers the following: - guidelines on what constitutes a cybersecurity incident - the types of cybersecurity incidents likely to be encountered and the expected response to each type - how to report cybersecurity incidents, internally to an organisation and externally to relevant authorities - other parties which need to be informed in the event of a cybersecurity incident - the authority, or authorities, responsible for investigating and responding to cybersecurity incidents - the criteria by which an investigation of a cybersecurity incident would be requested from a law enforcement agency, the Australian Signals Directorate or other relevant authority - the steps necessary to ensure the integrity of evidence relating to a cybersecurity incident - system contingency measures or a reference to such details if they are located in a separate document. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0912 | Systems have a change and configuration management plan that includes: - the establishment and maintenance of authorised baseline configurations for systems - what constitutes routine and urgent changes to the configuration of systems - how changes to the configuration of systems will be requested, tracked and documented - who needs to be consulted prior to routine and urgent changes to the configuration of systems - who needs to approve routine and urgent changes to the configuration of systems - who needs to be notified of routine and urgent changes to the configuration of systems - what additional change management and configuration management processes and procedures need to be followed before, during and after routine and urgent changes to the configuration of systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1163 | Systems have a continuous monitoring plan that includes: - conducting vulnerability scans for systems at least fortnightly - conducting vulnerability assessments and penetration tests for systems prior to deployment, including prior to deployment of significant changes, and at least annually thereafter - analysing identified vulnerabilities to determine their potential impact - implementing mitigations based on risk, effectiveness and cost. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1563 | At the conclusion of a security assessment for a system, a security assessment report is produced by the assessor and covers: - the scope of the security assessment - the system’s strengths and weaknesses - security risks associated with the operation of the system - the effectiveness of the implementation of controls - any recommended remediation actions. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1564 | At the conclusion of a security assessment for a system, a plan of action and milestones is produced by the system owner. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for physical security
8 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
8 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1973 | Non-classified systems are secured in suitably secure facilities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1974 | Non-classified servers, network devices and cryptographic equipment are secured in suitably secure server rooms or communications rooms. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1975 | Non-classified servers, network devices and cryptographic equipment are secured in suitably secure security containers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0813 | Server rooms, communications rooms and security containers are not left in unsecured states. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1074 | Keys or equivalent access mechanisms to server rooms, communications rooms and security containers are appropriately controlled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1296 | Physical security is implemented to protect network devices in public areas from physical damage or unauthorised access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0164 | Unauthorised people are prevented from observing systems, in particular workstation displays and keyboards, within facilities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0161 | IT equipment and media are secured when not in use. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for personnel security
42 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
42 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0252 | Cybersecurity awareness training is undertaken annually by all personnel and covers: - the purpose of the cybersecurity awareness training - security appointments and contacts - authorised use of systems and their resources - protection of systems and their resources - reporting of cybersecurity incidents and suspected compromises of systems and their resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1565 | Tailored privileged user training is undertaken annually by all privileged users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2022 | A cybersecurity awareness training register is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1740 | Personnel dealing with banking details and payment requests are advised of what business email compromise is, how to manage such situations and how to report it. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0817 | Personnel are advised of what suspicious contact via online services is and how to report it. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0820 | Personnel are advised to not post work information to unauthorised online services and to report cases where such information is posted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1146 | Personnel are advised to maintain separate work and personal user accounts for online services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0821 | Personnel are advised of security risks associated with posting personal information to online services and are encouraged to use any available privacy settings to restrict who can view such information. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0824 | Personnel are advised not to send or receive files via unauthorised online services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1864 | A system usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0432 | Access requirements for systems and their resources are documented in their system security plan. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0434 | Personnel undergo appropriate employment screening and, where necessary, hold an appropriate security clearance before being granted access to systems and their resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0435 | Personnel receive any necessary briefings before being granted access to systems and their resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1865 | Personnel agree to abide by system usage policies before being granted access to systems and their resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0414 | Personnel granted access to systems and their resources are uniquely identifiable. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0415 | The use of shared user accounts is strictly controlled, and personnel using such accounts are uniquely identifiable. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1583 | Personnel who are contractors are identified as such. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0405 | Requests for unprivileged access to systems and their resources are validated when first requested. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1852 | Unprivileged access to systems and their resources is limited to only what is required for users and services to undertake their duties. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1566 | Use of unprivileged access is centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1507 | Requests for privileged access to systems and their resources are validated when first requested. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1508 | Privileged access to systems and their resources is limited to only what is required for users and services to undertake their duties. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1175 | Privileged user accounts (excluding those explicitly authorised to access online services) are prevented from accessing the internet, email and web services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1883 | Privileged user accounts explicitly authorised to access online services are strictly limited to only what is required for users and services to undertake their duties. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1649 | Just-in-time administration is used for the administration of systems and their resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0445 | Privileged users are assigned a dedicated privileged user account to be used solely for duties requiring privileged access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1263 | Unique privileged user accounts are used for administering individual server applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1509 | Privileged access events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1650 | Privileged user account and security group management events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0430 | Access to systems and their resources are removed or suspended the same day personnel no longer have a legitimate requirement for access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1591 | Access to systems and their resources are removed or suspended as soon as practicable when personnel are detected undertaking malicious activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1404 | Unprivileged access to systems and their resources are disabled after 45 days of inactivity. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1648 | Privileged access to systems and their resources are disabled after 45 days of inactivity. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1647 | Privileged access to systems and their resources are disabled after 12 months unless revalidated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0407 | A secure record is maintained for the life of systems and their resources that covers the following for each user: - their user identification - their signed agreement to abide by system usage policies - who authorised their access - when their access was granted - the level of access they were granted - when their access, and their level of access, was last reviewed - when their level of access was changed, and to what extent (if applicable) - when their access was withdrawn (if applicable). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0441 | When personnel are granted temporary access to systems and their resources, effective controls are put in place to restrict their access to only data required for them to undertake their duties. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1610 | A method of emergency access to systems and their resources is documented and tested at least once when initially implemented and each time fundamental information technology infrastructure changes occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1611 | Break glass accounts are only used when normal authentication processes cannot be used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1612 | Break glass accounts are only used for specific authorised activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1614 | Break glass account credentials are changed by the account custodian after they are accessed by any other party. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1615 | Break glass accounts are tested after credentials are changed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1613 | Use of break glass accounts is centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for communications infrastructure
26 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
26 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0181 | Cabling infrastructure is installed in accordance with relevant Australian Standards, as directed by the Australian Communications and Media Authority. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1111 | Fibre-optic cables are used for cabling infrastructure instead of copper cables. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0211 | A cable register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0208 | A cable register contains the following for each cable: - cable identifier - cable colour - sensitivity/classification - source - destination - location - seal numbers (if applicable). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1645 | Floor plan diagrams are developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1646 | Floor plan diagrams contain the following: - cable paths (including ingress and egress points between floors) - cable reticulation system and conduit paths - floor concentration boxes - wall outlet boxes - network cabinets. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0206 | Cable labelling processes, and supporting cable labelling procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1096 | Cables are labelled at each end with sufficient source and destination details to enable the physical identification and inspection of the cable. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1639 | Building management cables are labelled with their purpose in black writing on a yellow background, with a minimum size of 2.5 cm x 1 cm, and attached at five-metre intervals. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1640 | Cables for foreign systems installed in Australian facilities are labelled at inspection points. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1820 | Cables for individual systems use a consistent colour. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0926 | Non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED cables are coloured neither salmon pink nor red. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1112 | Cables in non-TOP SECRET areas are inspectable every five metres or less. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1119 | Cables in TOP SECRET areas are fully inspectable for their entire length. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1114 | Cable bundles or conduits sharing a common cable reticulation system have a dividing partition or visible gap between each cable bundle and conduit. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1130 | In shared facilities, cables are run in an enclosed cable reticulation system. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1164 | In shared facilities, conduits or the front covers of ducts, cable trays in floors and ceilings, and associated fittings are clear plastic. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1115 | Cables from cable trays to wall outlet boxes are run in flexible or plastic conduit. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1095 | Wall outlet boxes denote the systems, cable identifiers and wall outlet box identifier. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1822 | Wall outlet boxes for individual systems use a consistent colour. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1107 | Non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED wall outlet boxes are coloured neither salmon pink nor red. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1109 | Wall outlet box covers are clear plastic. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1102 | Cable reticulation systems leading into cabinets are terminated as close as possible to the cabinet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1101 | In TOP SECRET areas, cable reticulation systems leading into cabinets in server rooms or communications rooms are terminated as close as possible to the cabinet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1103 | In TOP SECRET areas, cable reticulation systems leading into cabinets not in server rooms or communications rooms are terminated at the boundary of the cabinet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0250 | IT equipment meets industry and government standards relating to electromagnetic interference/electromagnetic compatibility. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for communications systems
34 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
34 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1078 | A telephone system usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0229 | Personnel are advised of the permitted sensitivity or classification of information that can be discussed over internal and external telephone systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0230 | Personnel are advised of security risks posed by non-secure telephone systems in areas where sensitive or classified conversations can occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0231 | When using cryptographic equipment to permit different levels of conversation for different kinds of connections, telephone systems give a visual indication of what kind of connection has been made. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0232 | Telephone systems used for sensitive or classified conversations encrypt all traffic that passes over external systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0233 | Cordless telephone handsets and headsets are not used for sensitive or classified conversations unless all communications are encrypted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0235 | Speakerphones are not used on telephone systems in TOP SECRET areas unless the telephone system is located in an audio secure room, the room is audio secure during conversations and only personnel involved in conversations are present in the room. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0236 | Off-hook audio protection features are used on telephone systems in areas where background conversations may exceed the sensitivity or classification that the telephone system is authorised for communicating. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0931 | In SECRET and TOP SECRET areas, push-to-talk handsets or push-to-talk headsets are used to meet any off-hook audio protection requirements. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1562 | Video conferencing and IP telephony infrastructure is hardened. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0546 | When video conferencing or IP telephony traffic passes through a gateway containing a firewall or proxy, a video-aware or voice-aware firewall or proxy is used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0548 | Video conferencing and IP telephony calls are established using a secure session initiation protocol. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0547 | Video conferencing and IP telephony calls are conducted using a secure real-time transport protocol. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0554 | An encrypted and non-replayable two-way authentication scheme is used for call authentication and authorisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0553 | Authentication and authorisation is used for all actions on a video conferencing network, including call setup and changing settings. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0555 | Authentication and authorisation is used for all actions on an IP telephony network, including registering a new IP phone, changing phone users, changing settings and accessing voicemail. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0551 | IP telephony is configured such that: - IP phones authenticate themselves to the call controller upon registration - auto-registration is disabled and only authorised devices are allowed to access the network - unauthorised devices are blocked by default - all unused and prohibited functionality is disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0549 | Video conferencing and IP telephony traffic is separated physically or logically from other data traffic. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0556 | Workstations are not connected to video conferencing units or IP phones unless the workstation or the device uses Virtual Local Area Networks or similar mechanisms to maintain separation between video conferencing, IP telephony and other data traffic. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0558 | IP phones used in public areas do not have the ability to access data networks, voicemail and directory services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0559 | Microphones (including headsets and USB handsets) and webcams are not used with non-SECRET workstations in SECRET areas. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1450 | Microphones (including headsets and USB handsets) and webcams are not used with non-TOP SECRET workstations in TOP SECRET areas. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1019 | A denial of service response plan for video conferencing and IP telephony services is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1805 | A denial of service response plan for video conferencing and IP telephony services contains the following: - how to identify signs of a denial-of-service attack - how to identify the source of a denial-of-service attack - how capabilities can be maintained during a denial-of-service attack - what actions can be taken to respond to a denial-of-service attack. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0588 | A fax machine and MFD usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1092 | Separate fax machines or MFDs are used for sending sensitive or classified fax messages and all other fax messages. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0241 | When sending fax messages, the fax message is encrypted to an appropriate level to be communicated over unsecured telecommunications infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1075 | The sender of a fax message makes arrangements for the receiver to collect the fax message as soon as possible after it is sent and for the receiver to notify the sender if the fax message does not arrive in an agreed amount of time. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0245 | A direct connection from an MFD to a digital telephone system is not enabled unless the digital telephone system is authorised to operate at the same sensitivity or classification as the network to which the MFD is connected. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1854 | Users authenticate to MFDs before they can print, scan or copy documents. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0590 | Authentication measures for MFDs are the same strength as those used for workstations on networks they are connected to. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0589 | MFDs are not used to scan or copy documents above the sensitivity or classification of networks they are connected to. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1855 | Use of MFDs for printing, scanning and copying purposes, including the capture of shadow copies of documents, are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1036 | Fax machines and MFDs are located in areas where their use can be observed. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for enterprise mobility
33 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
33 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1297 | Legal advice is sought prior to allowing privately-owned mobile devices and desktop computers to access systems or data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0874 | Mobile devices and desktop computers access the internet via a VPN connection to an organisation’s internet gateway rather than via a direct connection to the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0705 | When accessing an organisation’s network via a VPN connection, split tunnelling is disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1533 | A mobile device management policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1195 | Mobile Device Management solutions that have completed a Common Criteria evaluation against the Protection Profile for Mobile Device Management, version 4.0 or later, are used to enforce mobile device management policy. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0869 | Mobile devices encrypt their internal storage and any removable media. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1085 | Mobile devices encrypt all sensitive or classified data communicated over public network infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1886 | Mobile devices are configured to operate in a supervised (or equivalent) mode. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1887 | Mobile devices are configured with remote locate and wipe functionality. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1888 | Mobile devices are configured with secure lock screens. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0863 | Mobile devices prevent personnel from installing non-approved applications once provisioned. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0864 | Mobile devices prevent personnel from disabling or modifying security functionality once provisioned. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1366 | Security updates are applied to mobile devices as soon as they become available. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1082 | A mobile device usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1083 | Personnel are advised of the sensitivity or classification permitted for voice and data communications when using mobile devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1299 | Personnel are advised to take the following precautions when using mobile devices: - never leave mobile devices or removable media unattended, including by placing them in checked-in luggage or leaving them in hotel safes - never store credentials with mobile devices that they grant access to, such as in laptop computer bags - never lend mobile devices or removable media to untrusted people, even if briefly - never allow untrusted people to connect their mobile devices or removable media to your mobile devices, including for charging - never connect mobile devices to designated charging stations or wall outlet charging ports - never use gifted or unauthorised peripherals, chargers or removable media with mobile devices - never use removable media for data transfers or backups that have not been checked for malicious code beforehand - avoid reuse of removable media once used with other parties’ systems or mobile devices - avoid connecting mobile devices to open or untrusted Wi-Fi networks - consider disabling any communications capabilities of mobile devices when not in use, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Near Field Communication and ultra-wideband - consider periodically rebooting mobile devices - consider using a VPN connection to encrypt all cellular and wireless communications - consider using encrypted email or messaging apps for all communications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0240 | Paging, Multimedia Message Service, Short Message Service and messaging apps are not used to communicate sensitive or classified data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1196 | Non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED mobile devices are configured to remain undiscoverable to other Bluetooth devices except during Bluetooth pairing. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1200 | Bluetooth pairing for non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED mobile devices is performed using Secure Connections, preferably with Numeric Comparison if supported. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1198 | Bluetooth pairing for non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED mobile devices is performed in a manner such that connections are only made between intended Bluetooth devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1199 | Bluetooth pairings for non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED mobile devices are removed when there is no longer a requirement for their use. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0866 | Sensitive or classified data is not viewed on mobile devices in public locations unless care is taken to reduce the chance of the screen of a mobile device being observed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1644 | Sensitive or classified phone calls and conversations are not conducted in public locations unless care is taken to reduce the chance of conversations being overheard. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0871 | Mobile devices are kept under continual direct supervision when being actively used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0870 | Mobile devices are carried or stored in a secured state when not being actively used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1084 | If unable to carry or store mobile devices in a secured state, they are physically transferred in a security briefcase or an approved multi-use satchel, pouch or transit bag. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0701 | Mobile device emergency sanitisation processes, and supporting mobile device emergency sanitisation procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1298 | Personnel are advised of privacy and security risks when travelling overseas with mobile devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1554 | If travelling overseas with mobile devices to high or extreme risk countries, personnel are: - issued with newly provisioned user accounts, mobile devices and removable media from a pool of dedicated travel devices which are used solely for work-related activities - advised on how to apply and inspect tamper seals to key areas of mobile devices - advised to avoid taking any personal mobile devices, especially if rooted or jailbroken. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1555 | Before travelling overseas with mobile devices, personnel take the following actions: - record all details of the mobile devices being taken, such as product types, serial numbers and International Mobile Equipment Identity numbers - update all operating systems and applications - remove all non-essential data, applications and user accounts - backup all remaining data, applications and settings. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1088 | Personnel report the potential compromise of mobile devices, removable media or credentials to their organisation as soon as possible, especially if they: - provide credentials to foreign government officials - decrypt mobile devices for foreign government officials - have mobile devices taken out of sight by foreign government officials - have mobile devices or removable media stolen, including if later returned - lose mobile devices or removable media, including if later found - observe unusual behaviour of mobile devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1300 | Upon returning from travelling overseas with mobile devices, personnel take the following actions: - sanitise and reset mobile devices, including all removable media - decommission any credentials that left their possession during their travel - report if significant doubt exists as to the integrity of any mobile devices or removable media. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1556 | If returning from travelling overseas with mobile devices to high or extreme risk countries, personnel take the following additional actions: - reset credentials used with mobile devices, including those used for remote access to their organisation’s systems - monitor user accounts for any indicators of compromise, such as failed logon attempts. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for evaluated products
3 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
3 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0280 | If procuring an evaluated product, a product that has completed a PP-based evaluation, including against all applicable PP modules (as well as a software bill of materials assessment if applicable), is selected in preference to one that has completed an EAL-based evaluation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0285 | Evaluated products are delivered in a manner consistent with any delivery procedures defined in associated evaluation documentation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0289 | Evaluated products are installed, configured, administered and operated in an evaluated configuration and in accordance with vendor guidance. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for information technology equipment
31 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
31 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1551 | An IT equipment management policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1913 | Approved configurations for IT equipment are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1858 | IT equipment is hardened using ASD and vendor hardening guidance, with the most restrictive guidance taking precedence when conflicts occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0336 | A networked IT equipment register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1869 | A non-networked IT equipment register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0294 | IT equipment, with the exception of high assurance IT equipment, is labelled with protective markings reflecting its sensitivity or classification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0293 | IT equipment is classified based on the highest sensitivity or classification of data that it is approved for processing, storing or communicating. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1599 | IT equipment is handled in a manner suitable for its sensitivity or classification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0305 | Maintenance and repairs of IT equipment is carried out on site by an appropriately cleared technician. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0307 | If an appropriately cleared technician is not used to undertake maintenance or repairs of IT equipment, the IT equipment and associated media is sanitised before maintenance or repair work is undertaken. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0306 | If an appropriately cleared technician is not used to undertake maintenance or repairs of IT equipment, the technician is escorted by someone who: - is appropriately cleared and briefed - takes due care to ensure that data is not disclosed - takes all responsible measures to ensure the integrity of the IT equipment - has the authority to direct the technician - is sufficiently familiar with the IT equipment to understand the work being performed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0310 | IT equipment maintained or repaired off site is done so at facilities approved for handling the sensitivity or classification of the IT equipment. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1598 | Following maintenance or repair activities for IT equipment, the IT equipment is inspected to confirm it retains its approved configuration and that no unauthorised modifications have taken place. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0313 | IT equipment sanitisation processes, and supporting IT equipment sanitisation procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1741 | IT equipment destruction processes, and supporting IT equipment destruction procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0311 | IT equipment containing media is sanitised by removing the media from the IT equipment or by sanitising the media in situ. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1742 | IT equipment that cannot be sanitised is destroyed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0317 | At least three pages of random text with no blank areas are printed on each colour printer cartridge or MFD print drum. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1219 | MFD print drums and image transfer rollers are inspected and destroyed if there is remnant toner which cannot be removed or a print is visible on the image transfer roller. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1220 | Printer and MFD platens are inspected and destroyed if any text or images are retained on the platen. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1221 | Printers and MFDs are checked to ensure no pages are trapped in the paper path due to a paper jam. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0318 | When unable to sanitise printer cartridges or MFD print drums, they are destroyed as per electrostatic memory devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1534 | Printer ribbons in printers and MFDs are removed and destroyed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1076 | Televisions and computer monitors with minor burn-in or image persistence are sanitised by displaying a solid white image on the screen for an extended period of time. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1222 | Televisions and computer monitors that cannot be sanitised are destroyed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1223 | Memory in network devices is sanitised using the following processes, in order of preference: - following device-specific guidance provided in evaluation documentation - following vendor sanitisation guidance - loading a dummy configuration file, performing a factory reset and then reinstalling firmware. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1225 | The paper tray of the fax machine is removed, and a fax message with a minimum length of four pages is transmitted, before the paper tray is re-installed to allow a fax summary page to be printed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1226 | Fax machines are checked to ensure no pages are trapped in the paper path due to a paper jam. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1550 | IT equipment disposal processes, and supporting IT equipment disposal procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1217 | Labels and markings indicating the owner, sensitivity, classification or any other marking that can associate IT equipment with its prior use are removed prior to its disposal. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0316 | Following sanitisation, destruction or declassification, a formal administrative decision is made to release IT equipment, or its waste, into the public domain. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for media
45 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
45 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1549 | A media management policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1359 | A removable media usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1713 | A removable media register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0332 | Media, with the exception of internally mounted fixed media within information technology equipment, is labelled with protective markings reflecting its sensitivity or classification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0323 | Media is classified to the highest sensitivity or classification of data it stores, unless the media has been classified to a higher sensitivity or classification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0337 | Media is only used with systems that are authorised to process, store or communicate its sensitivity or classification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0325 | Any media connected to a system with a higher sensitivity or classification than the media is reclassified to the higher sensitivity or classification, unless the media is read-only or the system has a mechanism through which read-only access can be ensured. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0330 | Before reclassifying media to a lower sensitivity or classification, the media is sanitised or destroyed, and a formal administrative decision is made to reclassify it. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0831 | Media is handled in a manner suitable for its sensitivity or classification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1059 | All data stored on media is encrypted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1600 | Media is sanitised before it is used for the first time. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1642 | Media is sanitised before it is reused in a different security domain. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0347 | When transferring data manually between two systems belonging to different security domains, write-once media is used unless the destination system has a mechanism through which read-only access can be ensured. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0947 | When transferring data manually between two systems belonging to different security domains, rewritable media is sanitised after each data transfer. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0348 | Media sanitisation processes, and supporting media sanitisation procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0351 | Volatile media is sanitised by removing its power for at least 10 minutes. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0354 | Non-volatile magnetic media is sanitised by overwriting it at least once (or three times if pre-2001 or under 15 GB) in its entirety with a random pattern followed by a read back for verification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1065 | The host-protected area and device configuration overlay table are reset prior to the sanitisation of non-volatile magnetic hard drives. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1067 | The ATA secure erase command is used, in addition to block overwriting software, to ensure the growth defects table of non-volatile magnetic hard drives is overwritten. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0357 | Non-volatile EPROM media is sanitised by applying three times the manufacturer’s specified ultraviolet erasure time and then overwriting it at least once in its entirety with a random pattern followed by a read back for verification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0836 | Non-volatile EEPROM media is sanitised by overwriting it at least once in its entirety with a random pattern followed by a read back for verification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0359 | Non-volatile flash memory media is sanitised by overwriting it at least twice in its entirety with a random pattern followed by a read back for verification. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1735 | Media that cannot be successfully sanitised is destroyed prior to its disposal. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0363 | Media destruction processes, and supporting media destruction procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0350 | The following media types are destroyed prior to their disposal: - microfiche and microfilm - optical discs - programmable read-only memory - read-only memory - other types of media that cannot be sanitised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1361 | Security Construction and Equipment Committee-approved equipment or ASIO-approved equipment is used when destroying media. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1160 | If using degaussers to destroy media, degaussers evaluated by the United States’ National Security Agency are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1517 | Equipment that is capable of reducing microform to a fine powder, with resultant particles not showing more than five consecutive characters per particle upon microscopic inspection, is used to destroy microfiche and microfilm. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1722 | Electrostatic memory devices are destroyed using a furnace/incinerator, hammer mill, disintegrator or grinder/sander. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1723 | Magnetic floppy disks are destroyed using a furnace/incinerator, hammer mill, disintegrator, degausser or by cutting. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1724 | Magnetic hard disks are destroyed using a furnace/incinerator, hammer mill, disintegrator, grinder/sander or degausser. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1725 | Magnetic tapes are destroyed using a furnace/incinerator, hammer mill, disintegrator, degausser or by cutting. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1726 | Optical disks are destroyed using a furnace/incinerator, hammer mill, disintegrator, grinder/sander or by cutting. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1727 | Semiconductor memory is destroyed using a furnace/incinerator, hammer mill or disintegrator. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0368 | Media destroyed using a hammer mill, disintegrator, grinder/sander or by cutting results in media waste particles no larger than 9 mm. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0361 | Magnetic media is destroyed using a degausser with a suitable magnetic field strength and magnetic orientation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0362 | Product-specific directions provided by degausser manufacturers are followed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1641 | Following the use of a degausser, magnetic media is physically damaged by deforming any internal platters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0370 | The destruction of media is performed under the supervision of at least one cleared person. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0371 | Personnel supervising the destruction of media supervise its handling to the point of destruction and ensure that the destruction is completed successfully. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0372 | The destruction of media storing accountable material is performed under the supervision of at least two cleared personnel. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0373 | Personnel supervising the destruction of media storing accountable material supervise its handling to the point of destruction, ensure that the destruction is completed successfully and sign a destruction certificate afterwards. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0374 | Media disposal processes, and supporting media disposal procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0378 | Labels and markings indicating the owner, sensitivity, classification or any other marking that can associate media with its prior use are removed prior to its disposal. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0375 | Following sanitisation, destruction or declassification, a formal administrative decision is made to release media, or its waste, into the public domain. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for system hardening
205 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
205 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1743 | Vendors that have demonstrated a commitment to Secure by Design and Secure by Default principles and practices, including secure programming practices and either memory-safe programming languages or less preferably memory-safe programming practices, are used for operating systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1407 | The latest release, or the previous release, of operating systems are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1408 | Where supported, 64-bit versions of operating systems are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1406 | SOEs are used for workstations and servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1608 | SOEs provided by third parties are scanned for malicious code and configurations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1588 | SOEs are reviewed and updated at least annually. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1914 | Approved configurations for operating systems are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1409 | Operating systems are hardened using ASD and vendor hardening guidance, with the most restrictive guidance taking precedence when conflicts occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0383 | Default user accounts or credentials for operating systems, including for any pre-configured user accounts, are changed, disabled or removed during initial setup. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0380 | Unneeded user accounts, components, services and functionality of operating systems are disabled or removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0341 | Automatic execution features for removable media are disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1654 | Internet Explorer 11 is disabled or removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1655 | .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) is disabled or removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1492 | Operating system exploit protection functionality is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1745 | Early Launch Antimalware, Secure Boot, Trusted Boot and Measured Boot functionality is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1584 | Unprivileged users are prevented from bypassing, disabling or modifying security functionality of operating systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1491 | Unprivileged users are prevented from running script execution engines, including: - Windows Script Host (cscript.exe and wscript.exe) - PowerShell (powershell.exe, powershell_ise.exe and pwsh.exe) - Command Prompt (cmd.exe) - Windows Management Instrumentation (wmic.exe) - Microsoft Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Application Host (mshta.exe). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1592 | Unprivileged users do not have the ability to install unapproved applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0382 | Unprivileged users do not have the ability to uninstall or disable approved applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0843 | Application control is implemented on workstations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1490 | Application control is implemented on internet-facing servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1656 | Application control is implemented on non-internet-facing servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1870 | Application control is applied to user profiles and temporary folders used by operating systems, web browsers and email clients. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1871 | Application control is applied to all locations other than user profiles and temporary folders used by operating systems, web browsers and email clients. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1657 | Application control restricts the execution of executables, software libraries, scripts, installers, compiled HTML, HTML applications and control panel applets to an organisation-approved set. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1658 | Application control restricts the execution of drivers to an organisation-approved set. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0955 | Application control is implemented using cryptographic hash rules, publisher certificate rules or path rules. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1471 | When implementing application control using publisher certificate rules, publisher names and product names are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1392 | When implementing application control using path rules, only approved users can modify approved files and write to approved folders. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1746 | When implementing application control using path rules, only approved users can change file system permissions for approved files and folders. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1544 | Microsoft’s recommended application blocklist is implemented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1659 | Microsoft’s vulnerable driver blocklist is implemented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1582 | Application control rulesets are validated on an annual or more frequent basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0846 | All users (with the exception of local administrator accounts and break glass accounts) cannot disable, bypass or be exempted from application control. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1660 | Allowed and blocked application control events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1889 | Command line process creation events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1621 | Windows PowerShell 2.0 is disabled or removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1622 | PowerShell is configured to use Constrained Language Mode. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1623 | PowerShell module logging, script block logging and transcription events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1624 | PowerShell script block logs are protected by Protected Event Logging functionality. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1341 | A HIPS or EDR solution is implemented on workstations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1034 | A HIPS or EDR solution is implemented on critical servers and high-value servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1416 | A software firewall is implemented on workstations and servers to restrict inbound and outbound network connections to an organisation-approved set of applications and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1417 | An antivirus application is implemented on workstations and servers with: - signature-based detection functionality enabled and set to a high level - heuristic-based detection functionality enabled and set to a high level - reputation rating functionality enabled - ransomware protection functionality enabled - detection signatures configured to update on at least a daily basis - regular scanning configured for all fixed disks and removable media. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1418 | If there is no business requirement for reading from removable media and devices, such functionality is disabled via the use of a device access control application or by disabling external communication interfaces. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0343 | If there is no business requirement for writing to removable media and devices, such functionality is disabled via the use of a device access control application or by disabling external communication interfaces. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0345 | External communication interfaces that allow DMA are disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1976 | Security-relevant events for Apple macOS operating systems are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1977 | Security-relevant events for Linux operating systems are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0582 | Security-relevant events for Microsoft Windows operating systems are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0938 | Vendors that have demonstrated a commitment to Secure by Design and Secure by Default principles and practices, including secure programming practices and either memory-safe programming languages or less preferably memory-safe programming practices, are used for user applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1467 | The latest release of office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1915 | Approved configurations for user applications are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1806 | Default user accounts or credentials for user applications, including for any pre-configured user accounts, are changed, disabled or removed during initial setup. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1470 | Unneeded components, services and functionality of office productivity suites, web browsers, email clients, PDF applications and security products are disabled or removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1235 | Add-ons, extensions and plug-ins for office productivity suites, web browsers, email clients, PDF applications and security products are restricted to an organisation-approved set. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1667 | Microsoft Office is blocked from creating child processes. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1668 | Microsoft Office is blocked from creating executable content. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1669 | Microsoft Office is blocked from injecting code into other processes. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1542 | Microsoft Office is configured to prevent activation of Object Linking and Embedding packages. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1859 | Office productivity suites are hardened using ASD and vendor hardening guidance, with the most restrictive guidance taking precedence when conflicts occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1823 | Office productivity suite security settings cannot be changed by users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1486 | Web browsers do not process Java from the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1485 | Web browsers do not process web advertisements from the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1412 | Web browsers are hardened using ASD and vendor hardening guidance, with the most restrictive guidance taking precedence when conflicts occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1585 | Web browser security settings cannot be changed by users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1670 | PDF applications are blocked from creating child processes. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1860 | PDF applications are hardened using ASD and vendor hardening guidance, with the most restrictive guidance taking precedence when conflicts occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1824 | PDF application security settings cannot be changed by users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1601 | Microsoft’s attack surface reduction rules are implemented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1748 | Email client security settings cannot be changed by users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1825 | Security product security settings cannot be changed by users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1671 | Microsoft Office macros are disabled for users that do not have a demonstrated business requirement. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1488 | Microsoft Office macros in files originating from the internet are blocked. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1672 | Microsoft Office macro antivirus scanning is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1673 | Microsoft Office macros are blocked from making Win32 API calls. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1674 | Only Microsoft Office macros running from within a sandboxed environment, a Trusted Location or that are digitally signed by a trusted publisher are allowed to execute. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1890 | Microsoft Office macros are checked to ensure they are free of malicious code before being digitally signed or placed within Trusted Locations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1487 | Only privileged users responsible for checking that Microsoft Office macros are free of malicious code can write to and modify content within Trusted Locations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1675 | Microsoft Office macros digitally signed by an untrusted publisher cannot be enabled via the Message Bar or Backstage View. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1891 | Microsoft Office macros digitally signed by signatures other than V3 signatures cannot be enabled via the Message Bar or Backstage View. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1676 | Microsoft Office’s list of trusted publishers is validated on an annual or more frequent basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1489 | Microsoft Office macro security settings cannot be changed by users. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1826 | Vendors that have demonstrated a commitment to Secure by Design and Secure by Default principles and practices, including secure programming practices and either memory-safe programming languages or less preferably memory-safe programming practices, are used for server applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1483 | The latest release of internet-facing server applications are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1916 | Approved configurations for server applications are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1246 | Server applications are hardened using ASD and vendor hardening guidance, with the most restrictive guidance taking precedence when conflicts occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1260 | Default user accounts or credentials for server applications, including for any pre-configured user accounts, are changed, disabled or removed during initial setup. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1247 | Unneeded user accounts, components, services and functionality of server applications are disabled or removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1245 | All temporary installation files and logs created during server application installation processes are removed after server applications have been installed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1249 | Server applications are configured to run as a separate user account with the minimum privileges needed to perform their functions. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1250 | The user accounts under which server applications run have limited access to their underlying server’s file system. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1926 | Microsoft AD DS domain controllers, Microsoft AD CS CA servers, Microsoft AD FS servers and Microsoft Entra Connect servers are only used for their designed role and no other applications or services are installed, unless they are security related. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1927 | Access to Microsoft AD DS domain controllers, Microsoft AD CS CA servers, Microsoft AD FS servers and Microsoft Entra Connect servers is limited to privileged users that require access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1928 | Backups of Microsoft AD DS domain controllers, Microsoft AD CS CA servers, Microsoft AD FS servers and Microsoft Entra Connect servers are encrypted, stored securely and only accessible to backup administrator accounts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1830 | Security-relevant events for Microsoft AD DS domain controllers, Microsoft AD CS CA servers, Microsoft AD FS servers and Microsoft Entra Connect servers are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1827 | Microsoft AD DS domain controllers are administered using dedicated domain administrator user accounts that are not used to administer other systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1929 | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol signing is enabled on Microsoft AD DS domain controllers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1828 | The Print Spooler service is disabled on Microsoft AD DS domain controllers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1829 | Passwords are not stored in Group Policy Preferences. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1930 | Passwords are prevented from being stored in Group Policy Preferences. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1931 | SID Filtering is enabled for domain and forest trusts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1832 | Only service accounts and computer accounts are configured with Service Principal Names (SPNs). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1932 | The number of service accounts configured with an SPN is minimised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1933 | Service accounts configured with an SPN do not have DCSync permissions. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2010 | Service accounts configured with an SPN use the Advanced Encryption Standard for encryption. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1834 | Duplicate SPNs do not exist within the domain. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1833 | User accounts are provisioned with the minimum privileges required. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1934 | User accounts with DCSync permissions are reviewed at least annually, and those without an ongoing requirement for the permissions have them removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1835 | Privileged user accounts are configured as sensitive and cannot be delegated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1935 | Computer accounts are not configured for unconstrained delegation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1836 | User accounts require Kerberos pre-authentication. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1837 | User accounts are not configured with password never expires or password not required. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1838 | The UserPassword attribute for user accounts is not used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1936 | The sIDHistory attribute for user accounts is not used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1937 | User accounts are checked at least weekly for the presence of the sIDHistory attribute. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1839 | Account properties accessible by unprivileged users are not used to store passwords. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1840 | User account passwords do not use reversible encryption. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1841 | Unprivileged user accounts cannot add machines to the domain. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1842 | Dedicated privileged service accounts are used to add machines to the domain. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1843 | User accounts with unconstrained delegation are reviewed at least annually, and those without an SPN or demonstrated business requirement are removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1844 | Computer accounts that are not Microsoft AD DS domain controllers are not trusted for delegation to services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1938 | The Domain Computers security group does not have write or modify permissions to any Microsoft Active Directory objects. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1620 | Privileged user accounts are members of the Protected Users security group. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1939 | The number of user accounts that are members of the Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins or other highly-privileged security groups is minimised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1940 | Service accounts are not members of the Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins or other highly-privileged security groups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1941 | Computer accounts are not members of the Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins or other highly-privileged security groups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1942 | The Domain Computers security group is not a member of any privileged or highly-privileged security groups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1845 | When a user account is disabled, it is removed from all security group memberships. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1846 | The Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access security group does not contain user accounts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1943 | Strong mapping between certificates and users is enforced. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1944 | The EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2 flag is removed from Microsoft AD CS CA configurations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1945 | The CT_FLAG_ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT flag is removed from certificate templates. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1946 | Unprivileged user accounts do not have write access to certificate templates. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1947 | Extended Key Usages that enable user authentication are removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1948 | CA Certificate Manager approval is required for certificate templates that allow a Subject Alternative Name to be supplied. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1949 | Microsoft AD FS servers are administered using a dedicated service account that is not used to administer other systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1950 | Soft matching between Microsoft AD DS and Microsoft Entra ID is disabled following initial synchronisation activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1951 | Hard match takeover is disabled for Microsoft Entra Connect servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1952 | Privileged user accounts are not synchronised between Microsoft AD DS and Microsoft Entra ID. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1978 | Security-relevant events for server applications on internet-facing servers are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1979 | Security-relevant events for server applications on non-internet-facing servers are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1546 | Users are authenticated before they are granted access to a system and its resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1603 | Authentication methods susceptible to replay attacks are disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1055 | LAN Manager and NT LAN Manager authentication methods are disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1504 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users to their organisation’s online services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s sensitive data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1679 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users to third-party online services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s sensitive data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1680 | Multi-factor authentication (where available) is used to authenticate users to third-party online services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s non-sensitive data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1892 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users to their organisation’s online customer services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s sensitive customer data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1893 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users to third-party online customer services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s sensitive customer data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1681 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate customers to online customer services that process, store or communicate sensitive customer data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1919 | When multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users or customers to online services or online customer services, all other authentication protocols that do not support multi-factor authentication are disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1173 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate privileged users of systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0974 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate unprivileged users of systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1505 | Multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users of data repositories. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1401 | Multi-factor authentication uses either: something users have and something users know, or something users have that is unlocked by something users know or are. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1872 | Multi-factor authentication used for authenticating users of online services is phishing-resistant. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1873 | Multi-factor authentication used for authenticating customers of online customer services provides a phishing-resistant option. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1874 | Multi-factor authentication used for authenticating customers of online customer services is phishing-resistant. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1682 | Multi-factor authentication used for authenticating users of systems is phishing-resistant. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1894 | Multi-factor authentication used for authenticating users of data repositories is phishing-resistant. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1559 | Memorised secrets used for multi-factor authentication on non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED systems are a minimum of 6 characters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2011 | When phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication is used by user accounts, other non-phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication options are disabled for such user accounts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1920 | When multi-factor authentication is used to authenticate users to online services, online customer services, systems or data repositories – that process, store or communicate their organisation’s sensitive data or sensitive customer data – users are prevented from self-enrolling into multi-factor authentication from untrustworthy devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1683 | Successful and unsuccessful multi-factor authentication events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0417 | When systems cannot support multi-factor authentication, single-factor authentication using passphrases is implemented instead. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0421 | Passphrases used for single-factor authentication on non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive and PROTECTED systems are at least 4 random words with a total minimum length of 15 characters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1558 | Passphrases used for single-factor authentication are not a list of categorised words; do not form a real sentence in a natural language; and are not constructed from song lyrics, movies, literature or any other publicly available material. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1895 | Successful and unsuccessful single-factor authentication events are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1593 | Users provide sufficient evidence to verify their identity when requesting new credentials. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1227 | Credentials set for user accounts are randomly generated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1594 | Credentials are provided to users via a secure communications channel or, if not possible, split into two parts with one part provided to users and the other part provided to supervisors. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1595 | Credentials provided to users are changed on first use. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1596 | Credentials, in the form of memorised secrets, are not reused by users across different systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1953 | Credentials for the built-in Administrator account in each domain are long, unique, unpredictable and managed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1685 | Credentials for break glass accounts, local administrator accounts and service accounts are long, unique, unpredictable and managed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1795 | Credentials for built-in Administrator accounts, break glass accounts, local administrator accounts and service accounts are a minimum of 30 characters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1954 | Credentials for built-in Administrator accounts, break glass accounts, local administrator accounts and service accounts are randomly generated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1619 | Service accounts are created as group Managed Service Accounts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1590 | Credentials for user accounts are changed if: - they are compromised - they are suspected of being compromised - they are discovered stored on networks in the clear - they are discovered being transferred across networks in the clear - membership of a shared user account changes - they have not been changed in the past 12 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1955 | Credentials for computer accounts are changed if: - they are compromised - they are suspected of being compromised - they have not been changed in the past 30 days. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1847 | Credentials for the Kerberos Key Distribution Center’s service account (KRBTGT) are changed twice, allowing for replication to all Microsoft AD DS domain controllers in-between each change, if: - the domain has been directly compromised - the domain is suspected of being compromised - they have not been changed in the past 12 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1956 | Microsoft AD FS token-signing and encryption certificates are changed twice in quick succession if: - they are compromised - they are suspected of being compromised - they have not been changed in the past 12 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1597 | Credentials are obscured as they are entered into systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1980 | Credential hint functionality is not used for systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0418 | Physical credentials are kept separate from systems they are used to authenticate to, except for when performing authentication activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1402 | Credentials stored on systems are protected by a password manager; a hardware security module; or by salting, hashing and stretching them before storage within a database. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1957 | Private keys for Microsoft AD CS CA servers are protected by a hardware security module. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1896 | Memory integrity functionality is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1861 | Local Security Authority protection functionality is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1686 | Credential Guard functionality is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1897 | Remote Credential Guard functionality is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1749 | Cached credentials are limited to one previous logon. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1875 | Networks are scanned at least monthly to identify any credentials that are being stored in the clear. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1403 | User accounts, except for break glass accounts, are locked out after a maximum of five failed logon attempts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0853 | On a daily basis, outside of business hours and after an appropriate period of inactivity, user sessions are terminated and workstations are restarted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0428 | Services are configured with a session lock that: - activates after a maximum of 15 minutes of user inactivity, a maximum of 12 hours of overall session time or when manually activated by users - blocks access to all session content - requires users to re-authenticate using all authentication factors to unlock the session - denies users the ability to disable the session locking mechanism. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2012 | Systems are configured with a screen lock that: - activates after a maximum of 15 minutes of user inactivity, or when manually activated by users - conceals all content on the screen - ensures that the screen does not enter a power saving state before the screen lock is activated - requires users to re-authenticate using all authentication factors to unlock the system - denies users the ability to disable the screen locking mechanism. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0408 | Systems have a logon banner that reminds users of their security responsibilities when accessing the system and its resources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1460 | When using a software-based isolation mechanism to share a physical server’s hardware, the isolation mechanism is from a vendor that has demonstrated a commitment to Secure by Design and Secure by Default principles and practices, including secure programming practices and either memory-safe programming languages or less preferably memory-safe programming practices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1604 | When using a software-based isolation mechanism to share a physical server’s hardware, the configuration of the isolation mechanism is hardened by removing unneeded functionality and restricting access to the administrative interface used to manage the isolation mechanism. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1605 | When using a software-based isolation mechanism to share a physical server’s hardware, the underlying operating system is hardened. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1606 | When using a software-based isolation mechanism to share a physical server’s hardware, patches, updates or vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities are applied to the isolation mechanism and underlying operating system in a timely manner. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1848 | When using a software-based isolation mechanism to share a physical server’s hardware, the isolation mechanism or underlying operating system is replaced when it is no longer supported by a vendor. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1607 | When using a software-based isolation mechanism to share a physical server’s hardware, integrity monitoring and centralised event logging is performed for the isolation mechanism and underlying operating system. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for system management
67 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
67 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0042 | System administration processes, and supporting system administration procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1211 | System administrators perform system administration activities in accordance with the system’s change and configuration management plan. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1898 | Secure Admin Workstations are used in the performance of administrative activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1380 | Privileged users use separate privileged and unprivileged operating environments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1687 | Privileged operating environments are not virtualised within unprivileged operating environments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1688 | Unprivileged user accounts cannot logon to privileged operating environments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1689 | Privileged user accounts (excluding local administrator accounts) cannot logon to unprivileged operating environments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1958 | User accounts with DCSync permissions cannot logon to unprivileged operating environments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1385 | Administrative infrastructure is segregated from the wider network and the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1750 | Administrative infrastructure for critical servers, high-value servers and regular servers is segregated from each other. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1386 | Network management traffic can only originate from administrative infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1387 | Administrative activities are conducted through jump servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1899 | Network devices that do not belong to administrative infrastructure cannot initiate connections with administrative infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1143 | Patch management processes, and supporting patch management procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0298 | A centralised and managed approach that maintains the integrity of patches or updates, and confirms that they have been applied successfully, is used to patch or update applications, operating systems, drivers and firmware. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1493 | Software registers for workstations, servers, network devices and networked IT equipment are developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1643 | Software registers contain versions and patch histories of applications, drivers, operating systems and firmware. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1807 | An automated method of asset discovery is used at least fortnightly to support the detection of assets for subsequent vulnerability scanning activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1808 | A vulnerability scanner with an up-to-date vulnerability database is used for vulnerability scanning activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1698 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in online services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1699 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least weekly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1700 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1701 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1702 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1752 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of IT equipment other than workstations, servers and network devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1703 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in drivers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1900 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in firmware. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1921 | The likelihood of system compromise is frequently assessed when working exploits exist for unmitigated vulnerabilities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1876 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in online services are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1690 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in online services are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1691 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products are applied within two weeks of release. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1692 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1901 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1693 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, and security products are applied within one month of release. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1877 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1694 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1695 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within one month of release. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1696 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1902 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1878 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of IT equipment other than workstations, servers and network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1751 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of IT equipment other than workstations, servers and network devices are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1879 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1697 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1903 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in firmware are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1904 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in firmware are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as non-critical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1905 | Online services that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1704 | Office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0304 | Applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF applications, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1501 | Operating systems that are no longer supported by vendors are replaced. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1753 | Internet-facing network devices that are no longer supported by vendors are replaced. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1981 | Non-internet-facing network devices that are no longer supported by vendors are replaced. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1982 | Networked IT equipment that is no longer supported by vendors is replaced. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1809 | When applications, operating systems, network devices or networked IT equipment that are no longer supported by vendors cannot be immediately removed or replaced, compensating controls are implemented until such time that they can be removed or replaced. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1510 | A digital preservation policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1547 | Data backup processes, and supporting data backup procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1548 | Data restoration processes, and supporting data restoration procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1511 | Backups of data, applications and settings are performed and retained in accordance with business criticality and business continuity requirements. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1810 | Backups of data, applications and settings are synchronised to enable restoration to a common point in time. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1811 | Backups of data, applications and settings are retained in a secure and resilient manner. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1812 | Unprivileged user accounts cannot access backups belonging to other user accounts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1813 | Unprivileged user accounts cannot access their own backups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1705 | Privileged user accounts (excluding backup administrator accounts) cannot access backups belonging to other user accounts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1706 | Privileged user accounts (excluding backup administrator accounts) cannot access their own backups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1814 | Unprivileged user accounts are prevented from modifying and deleting backups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1707 | Privileged user accounts (excluding backup administrator accounts) are prevented from modifying and deleting backups. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1708 | Backup administrator accounts are prevented from modifying and deleting backups during their retention period. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1515 | Restoration of data, applications and settings from backups to a common point in time is tested as part of disaster recovery exercises. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for system monitoring
19 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
19 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0580 | An event logging policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1405 | A centralised event logging facility is implemented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1983 | Event logs sent to a centralised event logging facility are done so as soon as possible after they occur. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1984 | Event logs sent to a centralised event logging facility are encrypted in transit. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1985 | Event logs are protected from unauthorised access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1815 | Event logs are protected from unauthorised modification and deletion. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0988 | An accurate and consistent time source is used for event logging. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0585 | For each event logged, the date and time of the event, the relevant user or process, the relevant filename, the event description, and the information technology equipment involved are recorded. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1959 | To the extent possible, event logs are captured and stored in a consistent and structured format. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1986 | Event logs from critical servers are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1906 | Event logs from internet-facing servers are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1907 | Event logs from non-internet-facing servers are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0109 | Event logs from workstations are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1987 | Event logs from security products are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1960 | Event logs from internet-facing network devices are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1961 | Event logs from non-internet-facing network devices are analysed in a timely manner to detect cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1228 | Cybersecurity events are analysed in a timely manner to identify cybersecurity incidents. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1988 | Event logs are retained in a searchable manner for at least 12 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1989 | Event logs are retained as per minimum retention requirements for various classes of records as set out by the National Archives of Australia’s Administrative Functions Disposal Authority Express (AFDA Express) Version 2 publication. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for software development
89 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
89 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0400 | Development, testing, staging and production environments are segregated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1419 | Development and modification of software only takes place in development environments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1420 | Data from production environments is not used in non-production environments unless the non-production environment is secured to at least the same level as the production environment. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2023 | An authoritative source for software is established and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2024 | The authoritative source for software is used for all software development activities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1422 | Unauthorised access to the authoritative source for software is prevented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1816 | Unauthorised modification of the authoritative source for software is prevented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2025 | An issue tracking solution is used to link software development tasks to security issues and decisions, change or feature requests, programming issues, or bug fixes. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2026 | All software artefacts are scanned for malicious code before being imported into the authoritative source for software, including all compiled code, third-party libraries and software components. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2027 | All software artefacts are verified by a digital signature, or a secure hash provided over a secure channel, before being imported into the authoritative source for software. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2028 | All imported or referenced third-party software artefacts are tested using static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST) and software composition analysis (SCA) before being imported into the authoritative source for software and periodically throughout the software development life cycle. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2029 | The authoritative source for software restricts the use and import of third-party libraries and software components to trusted sources. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2030 | Scanning is used during commits to identify plain text or encoded secrets and keys, which are then blocked from being stored in the authoritative source for software. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2031 | Compilers, interpreters and build tools (including pipelines) that provide security features to improve executable file security are implemented and such security features are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2032 | The build solution ensures that all automated testing is completed without warnings, alerts or errors before building software artefacts. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2033 | All software security requirements are documented, stored securely and maintained throughout the software development life cycle. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2034 | Security design decisions are documented and reviewed throughout the software development cycle. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2035 | Security roles, responsibilities and knowledge requirements required to support the software development life cycle are identified and documented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2036 | Security responsibilities for software developers are identified and documented. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2037 | Software developers that lack sufficient cybersecurity knowledge and skills required for their projects or tasks undertake suitable training on secure software development and programming practices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2038 | A software developer cybersecurity knowledge and skills register is implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0401 | Secure by Design principles and practices are followed throughout the software development life cycle. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1238 | Threat modelling is used in support of the software development life cycle. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2039 | The software threat model is reviewed throughout the software development life cycle to ensure it reflects the as-built software and any changes to the threat environment. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2040 | Secure programming practices for the chosen programming language are used for software development. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2041 | Memory-safe programming languages, or less preferably memory-safe programming practices, are used for software development. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2042 | Secure by Default principles and practices are followed throughout the software development life cycle, including by ensuring that all built-in security measures are included and enabled in the base product at no extra cost to consumers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1780 | SecDevOps practices are used for software development. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2043 | Software is architected and structured to support readability and maintainability. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1922 | The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) Mobile Application Security Verification Standard is used in the development of mobile applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1923 | The OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications are mitigated in the development of large language model applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1924 | Large language model applications evaluate the sentence perplexity of user prompts to detect and mitigate adversarial suffixes designed to assist in the generation of sensitive or harmful content. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1796 | Files containing executable content are digitally signed by a certificate with a verifiable chain of trust as part of software development. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1797 | Installers, patches and updates are digitally signed or provided with cryptographic checksums as part of software development. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2044 | Software has no default credentials; however, if credentials are required, they are created on first install by the installing organisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2045 | Application backwards compatibility does not compromise any security measures or features. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2046 | Where software allows user impersonation, sensitive data is not logged and appropriate permissions are set. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2047 | Where software allows an authentication factor to be reset, the user is notified of the reset through a secondary channel. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2048 | Where software supports multiple user roles, non-administrative users are prevented from altering their profile permissions or privileges. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2049 | When user permissions or credentials are changed, software forces all impacted users to re-authenticate. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2050 | When digital signatures are processed by software, they are validated against a certificate trust chain and checked for revocation using a Certificate Revocation List or with the Online Certificate Status Protocol. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2051 | Software generates sufficient event logs to support the detection of cybersecurity events. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2052 | Event logs produced by software ensure that any sensitive data is protected. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1798 | Secure configuration guidance, in the form of a hardening guide or loosening guide, is produced and made available to consumers as part of software development. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2053 | End of life procedures for software, covering how to remove the software and how to archive or destroy any user accounts and data, are produced and made available to consumers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2054 | If a software bill of materials is available for imported third-party software components, it is used during software development to ensure such software components have no known vulnerabilities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1730 | A software bill of materials is produced and made available to consumers of software. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2055 | If a software build provenance is available for imported third-party software components, it is used during software development to ensure such software components are built to an appropriate standard. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2056 | A software build provenance is produced and made available to consumers of software. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1818 | Authentication and authorisation of clients is performed when clients call network APIs that facilitate modification of data and are accessible over the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2013 | Authentication and authorisation of clients is performed when clients call network APIs that facilitate modification of data but are not accessible over the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1817 | Authentication and authorisation of clients is performed when clients call network APIs that facilitate access to data not authorised for release into the public domain and are accessible over the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2014 | Authentication and authorisation of clients is performed when clients call network APIs that facilitate access to data not authorised for release into the public domain but are not accessible over the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1910 | Network API calls that facilitate modification of data, or access to data not authorised for release into the public domain, and are accessible over the internet, are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2015 | Network API calls that facilitate modification of data, or access to data not authorised for release into the public domain, but are not accessible over the internet, are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1240 | Validation and sanitisation are performed on all input received over the internet by software. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2016 | Validation and sanitisation are performed on all input received over a local network by software. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2057 | All input validation rules are documented, matched in code and tested with both positive and negative unit testing or integration testing. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2058 | Data sources and serialised data inputs are validated before being deserialised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2059 | File uploads or input are restricted to specific file types, with malicious content scanning occurring prior to file access, file execution or file storage. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1275 | All queries to databases from software are filtered for legitimate content and correct syntax. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1276 | Parameterised queries or stored procedures, instead of dynamically generated queries, are used by software for database interactions. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1278 | Software is designed or configured to provide as little error information as possible about the structure of databases. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1536 | All queries to databases from software that are initiated by users, and any resulting crash or error messages, are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0402 | Software is comprehensively tested for vulnerabilities, using SAST, DAST and SCA prior to its initial release, any subsequent releases and periodically in order to attempt to identify any previously unidentified vulnerabilities. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2060 | Code reviews are utilised to ensure software meets Secure by Design principles and practices as well as secure programming practices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2061 | Software developer-supported security-focused peer reviews are conducted on all critical and security-focused software components. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2062 | Unit testing and integration testing, covering both positive and negative use cases, are used to ensure code quality and security. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1616 | A vulnerability disclosure program is implemented to assist with the secure development and maintenance of products and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1755 | A vulnerability disclosure policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1756 | Vulnerability disclosure processes, and supporting vulnerability disclosure procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1717 | A ‘security.txt’ file is hosted for each of an organisation’s internet-facing website domains to assist in the responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities in the organisation’s products and services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1908 | Vulnerabilities identified in software are publicly disclosed in a responsible and timely manner, including with Common Weakness Enumeration and Common Platform Enumeration information. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1754 | Vulnerabilities identified in software are resolved in a timely manner. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1909 | In resolving vulnerabilities, root cause analysis is performed and, to the greatest extent possible, entire vulnerability classes are remediated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1911 | Security-relevant software crashes and error messages are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1239 | Robust web application frameworks are used in the development of web applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0971 | The OWASP Application Security Verification Standard is used in the development of web applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1849 | The OWASP Top 10 Proactive Controls are used in the development of web applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1850 | The OWASP Top 10 are mitigated in the development of web applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2063 | If supported, web application session cookies set the HttpOnly flag, Secure flag and the SameSite flag by default. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2064 | Web application session cookies contain only digitally signed opaque bearer tokens. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2065 | Web application session cookies using opaque bearer tokens that are not digitally signed use non-sequential random identifiers with a minimum of 128 bits of entropy, preferably 256 bits of entropy. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2066 | Web application sessions are centrally managed server side. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2067 | Web applications that support Single Sign On equally support Single Logout. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1424 | Content-Security-Policy, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Strict Transport Security and X-Frame-Options are specified by web server software via security policy in response headers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1552 | All web application content is offered exclusively using HTTPS. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1851 | The OWASP API Security Top 10 are mitigated in the development of web APIs. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1241 | Output encoding is performed on all output produced by web applications. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for database systems
13 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
13 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-1269 | Database servers and web servers are functionally separated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1277 | Data communicated between database servers and web servers is encrypted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1270 | Database servers are placed on a different network segment to user workstations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1271 | Network access controls are implemented to restrict database server communications to strictly defined network resources that require access to the database server. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1272 | If only local access to a database is required, networking functionality of database management system applications are disabled or directed to listen solely to the localhost interface. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1273 | Database servers for development, testing, staging and production environments are segregated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1243 | A database register is developed, implemented, maintained and verified on a regular basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1256 | File-based access controls are applied to database files. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0393 | Databases and their contents are classified based on the sensitivity or classification of data that they contain. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1255 | Database users’ ability to access, insert, modify and remove database contents is restricted based on their work duties. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1268 | The need-to-know principle is enforced for database contents through the application of minimum privileges, database views, database roles and data tokenisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1274 | Database contents from production environments are not used in non-production environments unless the non-production environment is secured to at least the same level as the production environment. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1537 | Security-relevant events for databases are centrally logged, including: - access or modification of particularly important content - addition of new users, especially privileged users - changes to user roles or privileges - attempts to elevate user privileges - queries containing comments - queries containing multiple embedded queries - database and query alerts or failures - database structure changes - database administrator actions - use of executable commands - database logons and logoffs. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for email
25 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
25 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0264 | An email usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0267 | Access to non-approved webmail services is blocked. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0270 | Protective markings are applied to emails and reflect the highest sensitivity or classification of the subject, body and attachments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0271 | Protective marking tools do not automatically insert protective markings into emails. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0272 | Protective marking tools do not allow users to select protective markings that a system has not been authorised to process, store or communicate. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1089 | Protective marking tools do not allow users replying to or forwarding emails to select protective markings lower than previously used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0565 | Email servers are configured to block, log and report emails with inappropriate protective markings. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1023 | The intended recipients of blocked inbound emails, and the senders of blocked outbound emails, are notified. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0569 | Emails are routed via centralised email gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0571 | When users send or receive emails, an authenticated and encrypted channel is used to route emails via their organisation’s centralised email gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0570 | Where backup or alternative email gateways are in place, they are maintained at the same standard as the primary email gateway. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0567 | Email servers only relay emails destined for or originating from their domains (including subdomains). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0572 | Opportunistic TLS encryption is enabled on email servers that make incoming or outgoing email connections over public network infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1589 | MTA-STS is enabled to prevent the unencrypted transfer of emails between email servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0574 | SPF is used to specify authorised email servers (or lack thereof) for an organisation’s domains (including subdomains). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1183 | A hard fail SPF record is used when specifying authorised email servers (or lack thereof) for an organisation’s domains (including subdomains). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1151 | SPF is used to verify the authenticity of incoming emails. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0861 | DKIM signing is enabled on emails originating from an organisation’s domains (including subdomains). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1026 | DKIM signatures on incoming emails are verified. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1027 | Email distribution list applications used by external senders is configured such that it does not break the validity of the sender’s DKIM signature. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1540 | DMARC records are configured for an organisation’s domains (including subdomains) such that emails are rejected if they do not pass DMARC checks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1799 | Incoming emails are rejected if they do not pass DMARC checks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1234 | Email content filtering is implemented to filter potentially harmful content in email bodies and attachments. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1502 | Emails arriving via an external connection where the email source address uses an internal domain, or internal subdomain, are blocked at the email gateway. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1024 | Notifications of undeliverable emails are only sent to senders that can be verified via SPF or other trusted means. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for networking
70 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
70 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0518 | Network documentation is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0516 | Network documentation includes high-level network diagrams showing all connections into networks and logical network diagrams showing all critical servers, high-value servers, network devices and network security appliances. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1912 | Network documentation includes device settings for all critical servers, high-value servers, network devices and network security appliances. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1178 | Network documentation provided to a third party, or published in public tender documentation, only contains details necessary for other parties to undertake contractual services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1181 | Networks are segregated into multiple network zones according to the criticality of servers, services and data. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1577 | An organisation’s networks are segregated from their service providers’ networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1532 | VLANs are not used to separate network traffic between an organisation’s networks and public network infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0529 | VLANs are not used to separate network traffic between networks belonging to different security domains. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0530 | Network devices managing VLANs are administered from the most trusted security domain. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0535 | Network devices managing VLANs belonging to different security domains do not share VLAN trunks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1364 | Network devices managing VLANs terminate VLANs belonging to different security domains on separate physical network interfaces. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2068 | Internet connectivity for networked devices is strictly limited to those that require access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1863 | Networked management interfaces for IT equipment are not directly exposed to the internet. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0385 | Servers maintain effective functional separation with other servers allowing them to operate independently. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1479 | Servers minimise communications with other servers at the network and file system level. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1781 | All data communicated over network infrastructure is encrypted. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0521 | IPv6 functionality is disabled in dual-stack network devices unless it is being used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1186 | IPv6 capable network security appliances are used on IPv6 and dual-stack networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1428 | Unless explicitly required, IPv6 tunnelling is disabled on all network devices. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1429 | IPv6 tunnelling is blocked by network security appliances at externally-connected network boundaries. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1430 | Dynamically assigned IPv6 addresses are configured with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6 in a stateful manner with lease data stored in a centralised event logging facility. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0520 | Network access controls are implemented on networks to prevent the connection of unauthorised network devices and networked IT equipment. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1182 | Network access controls are implemented to limit the flow of network traffic within and between network segments to only that required for business purposes. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1006 | Security measures are implemented to prevent unauthorised access to network management traffic. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1962 | SMB version 1 is not used on networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1311 | SNMP version 1 and SNMP version 2 are not used on networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1312 | All default SNMP community strings on network devices are changed and write access is disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1028 | A NIDS or NIPS is deployed in gateways between an organisation’s networks and other networks they do not manage. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1030 | A NIDS or NIPS is located immediately inside the outermost firewall for gateways and configured to generate event logs and alerts for network traffic that contravenes any rule in a firewall ruleset. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1627 | Inbound network connections from anonymity networks are blocked. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1628 | Outbound network connections to anonymity networks are blocked. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2017 | DNS traffic is encrypted by clients and servers wherever supported. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1782 | A protective DNS service is used to block access to known malicious domain names. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1800 | Network devices are flashed with trusted firmware before they are used for the first time. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1304 | Default user accounts or credentials for network devices, including for any pre-configured user accounts, are changed, disabled or removed during initial setup. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0534 | Unused physical ports on network devices are disabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1801 | Network devices are restarted on at least a monthly basis. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1963 | Security-relevant events for internet-facing network devices are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1964 | Security-relevant events for non-internet-facing network devices are centrally logged. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1314 | All wireless devices are Wi-Fi Alliance certified. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0536 | Public wireless networks provided for general public use are segregated from all other organisation networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1315 | The administrative interface on wireless access points is disabled for wireless network connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1710 | Settings for wireless access points are hardened. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1316 | Default SSIDs of wireless access points are changed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1317 | SSIDs of non-public wireless networks are not readily associated with an organisation, the location of their premises or the functionality of wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1318 | SSID broadcasting is not disabled on wireless access points. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1320 | MAC address filtering is not used to restrict which devices can connect to wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1319 | Static addressing is not used for assigning IP addresses on wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1332 | WPA3-Enterprise 192-bit mode is used to protect the confidentiality and integrity of all wireless network traffic. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1321 | 802.1X authentication with EAP-TLS, using X.509 certificates, is used for mutual authentication; with all other EAP methods disabled on supplicants and authentication servers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1711 | User identity confidentiality is used if available with EAP-TLS implementations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1322 | Evaluated supplicants, authenticators, wireless access points and authentication servers are used in wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1324 | Certificates are generated using an evaluated certificate authority or hardware security module. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1323 | Certificates are required for devices and users accessing wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1327 | Certificates are protected by logical and physical access controls, encryption, and user authentication. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1330 | The PMK caching period is not set to greater than 1440 minutes (24 hours). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1712 | The use of FT (802.11r) is disabled unless authenticator-to-authenticator communications are secured by an ASD-Approved Cryptographic Protocol. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1454 | Communications between authenticators and a RADIUS server are encapsulated with an additional layer of encryption using RADIUS over Internet Protocol Security or RADIUS over Transport Layer Security. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1334 | Wireless networks implement sufficient frequency separation from other wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1335 | Wireless access points enable the use of the 802.11w amendment to protect management frames. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1338 | Instead of deploying a small number of wireless access points that broadcast on high power, a greater number of wireless access points that use less broadcast power are deployed to achieve the desired footprint for wireless networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1437 | Cloud service providers are used for hosting online services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1579 | Cloud service providers’ ability to dynamically scale resources in response to a genuine spike in demand is discussed and verified as part of capacity and availability planning for online services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1580 | Where a high availability requirement exists for online services, the services are architected to automatically transition between availability zones. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1581 | Continuous real-time monitoring of the capacity and availability of online services is performed. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1438 | Where a high availability requirement exists for website hosting, CDNs that cache websites are used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1439 | If using CDNs, disclosing the IP addresses of web servers under an organisation’s control (referred to as origin servers) is avoided and access to the origin servers is restricted to the CDNs and authorised management networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1431 | Denial-of-service attack mitigation strategies are discussed with cloud service providers, specifically: - their capacity to withstand denial-of-service attacks - costs likely to be incurred as a result of denial-of-service attacks - availability monitoring and thresholds for notification of denial-of-service attacks - thresholds for turning off any online services or functionality during denial-of-service attacks - pre-approved actions that can be undertaken during denial-of-service attacks - any arrangements with upstream service providers to block malicious network traffic as far upstream as possible. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1436 | Critical online services are segregated from other online services that are more likely to be targeted as part of denial-of-service attacks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1432 | Domain names for online services are protected via registrar locking and confirming that domain registration details are correct. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for cryptography
57 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
57 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0507 | Cryptographic key management processes, and supporting cryptographic key management procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1080 | An ASD-Approved Cryptographic Algorithm (AACA) or high assurance cryptographic algorithm is used when encrypting media. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0459 | Full disk encryption, or partial encryption where access controls will only allow writing to the encrypted partition, is implemented when encrypting data at rest. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0469 | An ASD-Approved Cryptographic Protocol (AACP) or high assurance cryptographic protocol is used to protect data when communicated over network infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0455 | Where practical, cryptographic equipment and applications provide a means of data recovery to allow for circumstances where the encryption key is unavailable due to loss, damage or failure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0462 | When a user authenticates to the encryption functionality of IT equipment or media, it is treated in accordance with its original sensitivity or classification until the user deauthenticates from the encryption functionality. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0501 | Keyed cryptographic equipment is transported based on the sensitivity or classification of its keying material. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0142 | The compromise or suspected compromise of cryptographic equipment or associated keying material is reported to the chief information security officer, or one of their delegates, as soon as possible after it occurs. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1091 | Keying material is changed when compromised or suspected of being compromised. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0471 | Only AACAs or high assurance cryptographic algorithms are used by cryptographic equipment and applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0994 | ECDH is used in preference to DH. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0472 | When using DH for agreeing on encryption session keys, a modulus of at least 2048 bits is used, preferably 3072 bits. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1629 | When using DH for agreeing on encryption session keys, a modulus and associated parameters are selected according to NIST SP 800-56A Rev. 3. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1446 | When using elliptic curve cryptography, a suitable curve from NIST SP 800-186 is used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0474 | When using ECDH for agreeing on encryption session keys, a base point order and key size of at least 224 bits is used, preferably the NIST P-384 curve. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0475 | When using ECDSA for digital signatures, a base point order and key size of at least 224 bits is used, preferably the P-384 curve. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1990 | When using ML-DSA and ML-KEM, as per FIPS 204 and FIPS 203 respectively, adherence to pre-requisite FIPS publications is preferred. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1991 | When using ML-DSA for digital signatures, ML-DSA-65 or ML-DSA-87 is used, preferably ML-DSA-87. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1992 | When using ML-DSA for digital signatures, the hedged variant is used whenever possible. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1993 | Pre-hashed variants of ML-DSA-65 and ML-DSA-87 are only used when the performance of default variants is unacceptable. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1994 | When the pre-hashed variants of ML-DSA-65 and ML-DSA-87 are used, at least SHA-384 and SHA-512 respectively are used for pre-hashing. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1995 | When using ML-KEM for encapsulating encryption session keys (and similar keys), ML-KEM-768 or ML-KEM-1024 is used, preferably ML-KEM-1024. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0476 | When using RSA for digital signatures, and transporting encryption session keys (and similar keys), a modulus of at least 2048 bits is used, preferably 3072 bits. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0477 | When using RSA for digital signatures, and for transporting encryption session keys (and similar keys), a different key pair is used for digital signatures and transporting encryption session keys. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1766 | When using SHA-2 for hashing, an output size of at least 224 bits is used, preferably SHA-384 or SHA-512. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1769 | When using AES for encryption, AES-128, AES-192 or AES-256 is used, preferably AES-256. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0479 | Symmetric cryptographic algorithms are not used in Electronic Codebook Mode. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1917 | The development and procurement of new cryptographic equipment and applications ensures support for the use of ML-DSA-87, ML-KEM-1024, SHA-384, SHA-512 and AES-256 by no later than 2030. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1996 | When a post-quantum traditional hybrid scheme is used, either the post-quantum cryptographic algorithm, the traditional cryptographic algorithm or both are AACAs. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0481 | Only AACPs or high assurance cryptographic protocols are used by cryptographic equipment and applications. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1139 | Only the latest version of TLS is used for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1369 | AES-GCM is used for encryption of TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1370 | Only server-initiated secure renegotiation is used for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1372 | DH or ECDH is used for key establishment of TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1448 | When using DH or ECDH for key establishment of TLS connections, the ephemeral variant is used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1373 | Anonymous DH is not used for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1374 | SHA-2-based certificates are used for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1375 | SHA-2 is used for the Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) and pseudorandom function (PRF) for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1553 | TLS compression is disabled for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1453 | Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) is used for TLS connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1506 | The use of SSH version 1 is disabled for SSH connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0484 | The SSH daemon is configured to: - only listen on the required interfaces (ListenAddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) - have a suitable login banner (Banner x) - have a login authentication timeout of no more than 60 seconds (LoginGraceTime 60) - disable host-based authentication (HostbasedAuthentication no) - disable rhosts-based authentication (IgnoreRhosts yes) - disable the ability to login directly as root (PermitRootLogin no) - disable empty passwords (PermitEmptyPasswords no) - disable connection forwarding (AllowTCPForwarding no) - disable gateway ports (GatewayPorts no) - disable X11 forwarding (X11Forwarding no). | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0485 | Public key-based authentication is used for SSH connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1449 | SSH private keys are protected with a passphrase or a key encryption key. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0487 | When using logins without a passphrase for SSH connections, the following are disabled: - access from IP addresses that do not require access - port forwarding - agent credential forwarding - X11 forwarding - console access. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0488 | If using remote access without the use of a passphrase for SSH connections, the ‘forced command’ option is used to specify what command is executed and parameter checking is enabled. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0489 | When SSH-agent or similar key caching applications are used, it is limited to workstations and servers with screen locks and key caches that are set to expire within four hours of inactivity. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0490 | Versions of S/MIME earlier than S/MIME version 3.0 are not used for S/MIME connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0494 | Tunnel mode is used for IPsec connections; however, if using transport mode, an IP tunnel is used. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0496 | The ESP protocol is used for authentication and encryption of IPsec connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1233 | IKE version 2 is used for key exchange when establishing IPsec connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1771 | AES is used for encrypting IPsec connections, preferably ENCR_AES_GCM_16. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1772 | PRF_HMAC_SHA2_256, PRF_HMAC_SHA2_384 or PRF_HMAC_SHA2_512 is used for IPsec connections, preferably PRF_HMAC_SHA2_512. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0998 | AUTH_HMAC_SHA2_256_128, AUTH_HMAC_SHA2_384_192, AUTH_HMAC_SHA2_512_256 or NONE (only with AES-GCM) is used for authenticating IPsec connections, preferably NONE. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0999 | DH or ECDH is used for key establishment of IPsec connections, preferably 384-bit random ECP group, 3072-bit MODP Group or 4096-bit MODP Group. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0498 | A security association lifetime of less than four hours (14400 seconds) is used for IPsec connections. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1000 | PFS is used for IPsec connections. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for gateways
48 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
48 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0628 | Gateways are implemented between networks belonging to different security domains. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0637 | Gateways implement a demilitarised zone if external parties require access to an organisation’s services. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0631 | Gateways only allow explicitly authorised data flows. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1192 | Gateways inspect and filter data flows at the transport and above network layers. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1427 | Gateways perform ingress traffic filtering to detect and prevent IP source address spoofing. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1520 | System administrators for gateways undergo appropriate employment screening, and where necessary hold an appropriate security clearance, based on the sensitivity or classification of gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0611 | System administrators for gateways are assigned the minimum privileges required to perform their duties. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0616 | Separation of duties is implemented in performing administrative activities for gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0612 | System administrators for gateways are formally trained on the operation and management of gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1774 | Gateways are managed via a secure path isolated from all connected networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0629 | For gateways between networks belonging to different security domains, any shared components are managed by system administrators for the higher security domain or by system administrators from a mutually agreed upon third party. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0619 | Users authenticate to other networks accessed via gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0622 | IT equipment authenticates to other networks accessed via gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1783 | Public IP addresses controlled by, or used by, an organisation are signed by valid ROA records. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-2018 | Routes for RPKI-registered IP addresses that are advertised from invalid Autonomous Systems, or that are longer than allowed, are rejected or deprioritised by routers that exchange routes via BGP. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0634 | Security-relevant events for gateways are centrally logged, including: - data packets and data flows permitted through gateways - data packets and data flows attempting to leave gateways - real-time alerts for attempted intrusions. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1037 | Gateways undergo testing following configuration changes, and at regular intervals no more than six months apart, to validate they conform to expected security configurations. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0100 | Non-classified, OFFICIAL: Sensitive, PROTECTED and SECRET gateways undergo an IRAP assessment, using the latest release of the ISM available prior to the beginning of the IRAP assessment (or a subsequent release), at least every 24 months. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1528 | Evaluated firewalls are used between an organisation’s networks and public network infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0639 | Evaluated firewalls are used between networks belonging to different security domains. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1862 | If using a WAF, disclosing the IP addresses of web servers under an organisation’s control (referred to as origin servers) is avoided and access to the origin servers is restricted to the WAF and authorised management networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0643 | Evaluated diodes are used for controlling the data flow of unidirectional gateways between an organisation’s networks and public network infrastructure. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1157 | Evaluated diodes are used for controlling the data flow of unidirectional gateways between networks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0258 | A web usage policy is developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0260 | All web access, including that by internal servers, is conducted through web proxies. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0261 | The following details are centrally logged for websites accessed via web proxies: - web address - date and time - user - amount of data uploaded and downloaded - internal and external IP addresses. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0963 | Web content filtering is implemented to filter potentially harmful web-based content. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0961 | Client-side active content is restricted by web content filters to an organisation-approved list of domain names. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1237 | Web content filtering is applied to outbound web traffic where appropriate. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0263 | TLS traffic communicated through gateways is decrypted and inspected. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0958 | An organisation-approved list of domain names, or list of website categories, is implemented for all Hypertext Transfer Protocol and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure traffic communicated through gateways. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1236 | Malicious domain names, dynamic domain names and domain names that can be registered anonymously for free are blocked by web content filters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1171 | Attempts to access websites through their IP addresses instead of their domain names are blocked by web content filters. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0659 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs undergo content filtering checks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0651 | Files identified by content filtering checks as malicious, or that cannot be inspected, are blocked. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0652 | Files identified by content filtering checks as suspicious are quarantined until reviewed and subsequently approved or not approved for release. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1293 | Encrypted files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs are decrypted in order to undergo content filtering checks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1289 | Archive files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs are unpacked in order to undergo content filtering checks. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1290 | Archive files are unpacked in a controlled manner to ensure content filter performance or availability is not adversely affected. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1288 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs undergo antivirus scanning using multiple different scanning engines. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1389 | Executable files imported via gateways or CDSs are automatically executed in a sandbox to detect any suspicious behaviour. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0649 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs are filtered for allowed file types. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1284 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs undergo content validation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1965 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs undergo content checking. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1286 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs undergo content conversion. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1287 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs undergo content sanitisation. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0677 | Files imported or exported via gateways or CDSs that have a digital signature or cryptographic checksum are validated. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0591 | Evaluated peripheral switches are used when sharing peripherals between systems. | Not Assessed |
Guidelines for data transfers
8 controls 0 implemented,
0 partial,
0 not implemented,
8 not assessed
▼
| ISM CONTROL | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ISM-0663 | Data transfer processes, and supporting data transfer procedures, are developed, implemented and maintained. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0661 | Users transferring data to and from systems are held accountable for data transfers they perform. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-0657 | When manually importing data to systems, the data is scanned for malicious and active content. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1778 | When manually importing data to systems, all data that fails security checks is quarantined until reviewed and subsequently approved or not approved for release. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1187 | When manually exporting data from systems, the data is checked for unsuitable protective markings. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1779 | When manually exporting data from systems, all data that fails security checks is quarantined until reviewed and subsequently approved or not approved for release. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1586 | Data transfer logs are used to record all data imports and exports from systems. | Not Assessed |
| ISM-1294 | Data transfer logs for systems are partially verified at least monthly. | Not Assessed |